How to Set Up Traffic Protection and Filtering: Sensors, Lists, and Advanced Rules
Once the service is activated, it will appear on your account’s main page and in the My Services section. To start configuring it, simply click the service name to open the settings panel.

In the settings, find the object you want to configure and click its row, which displays a small graph thumbnail.
In the left-hand menu, select Protection.
On the page that opens, you can configure the parameters:
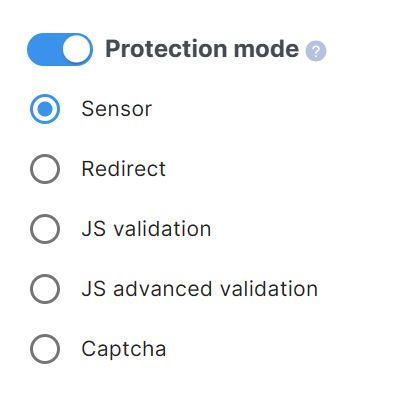
Protection mode
- Sensor
The sensor monitors the total number of requests, spikes, and errors while the filters remain in passive mode. If an attack is detected, the sensor activates the filters to mitigate it. The sensor’s response time usually does not exceed one minute but may vary depending on the attack’s intensity.
- Redirect
For visitor requests, an additional redirect to the requested location is applied.
- JS validation
For requests from regular IP addresses, validation is performed using JavaScript.
- JS advanced validation
For requests from regular IP addresses, advanced validation using JavaScript is applied.
- Captcha
A request to the site will require passing a Captcha for validation.
Proactive protection
The protection is based on a positive security model. Any users whose behavior does not match this model can either be blocked or subjected to additional checks (depending on the configured settings).
When proactive protection is enabled in sensor mode, requests are not filtered, but each new visitor is evaluated against multiple parameters:
- Pages visited on the site
- Use of keep-alive connections
- Presence of attacks on other sites
- Whether request limits are exceeded
- Which User Agents are used
- Other indicators
If violations are detected, the user’s behavior continues to be monitored. Selective validation makes it possible to avoid switching the entire configuration into active mode.

Cookie
To enhance security, you can limit the duration of user sessions. Shorter session lifetimes reduce the window of opportunity for unauthorized actions if someone gains illicit access to the resource.
When the configured time expires, users will be required to re-authenticate. By default, this parameter is set to 30 minutes.
Clicking the Generate New Security Key button will force all active users to revalidate their sessions.
Note: The lifetime of the cookies used by the security system does not affect website session durations. The system does not modify the website’s original cookies.

Whitelist
Requests from the addresses specified here will be transmitted without filtering.
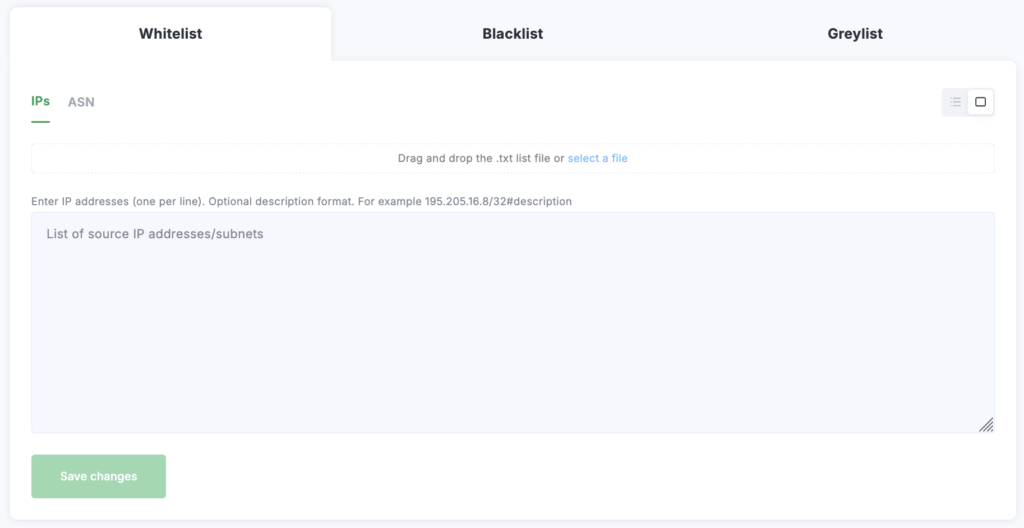
Fill out the form to add a new address to the list. You can also upload addresses from a “.txt” file, with each address on a separate line.
You can add individual addresses (for example, 8.8.8.8) or specify a network with a mask (for example, 8.8.8.0/24). On the ASN tab, you can add AS numbers in a similar manner.
Blacklist
A user with an address from this list will receive an HTTP 403 Forbidden error when attempting to access your resource. You can add a new address to the list in the same way as for the Whitelist.
Greylist
For individual IPs or subnets specified in this list, you can assign a unique protection method that differs from the one applied to other addresses. You can add a new address to the list using the same procedure as for the Whitelist.
Geolocation Filter
Here, you can restrict access to your resource based on the visitor’s country of origin.
Click the Add Country button and fill out the form. The countries are available from a dropdown list.
When using L3 and L7 filtering without SSL decryption, you can add no more than 15 countries per rule. For L7 filtering with SSL decryption, there are no limits on the number of countries.
All added parameters will appear in the form. You can assign a specific protection level to any countries selected from the list.
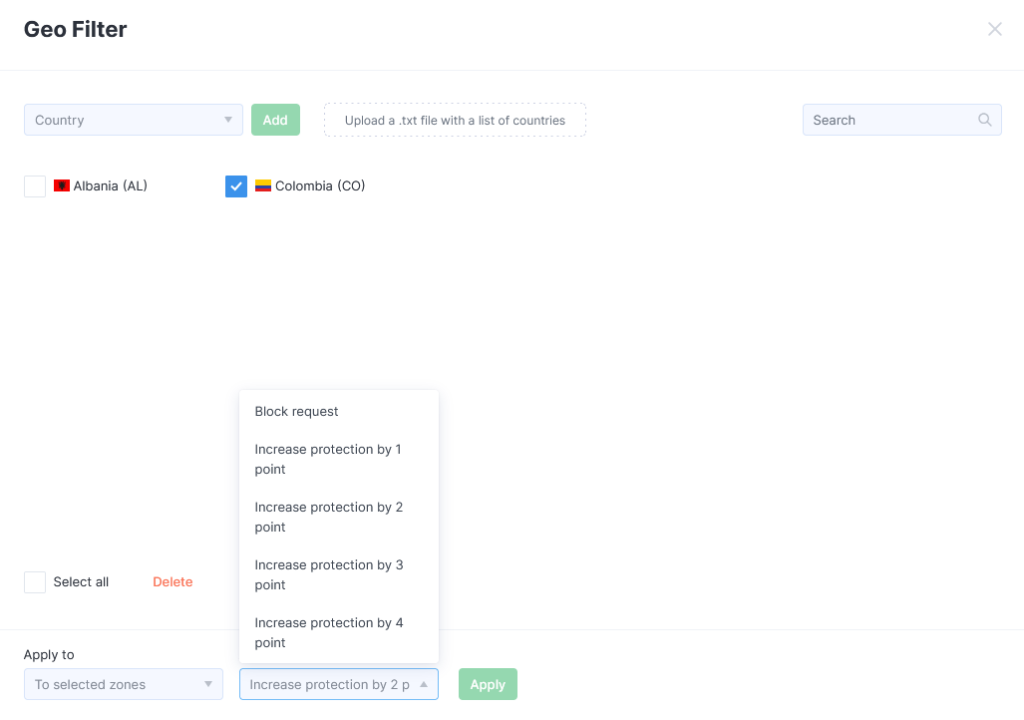
The protection level escalates incrementally from the current state:
- SENSOR
- REDIRECT
- JS
- JSA
- CAPTCHA
If the current protection method is REDIRECT:
Exceptions by location
For certain requests, you can disable the use of interactive checks. For example, if only bots or mobile applications access a particular server resource, requiring a check could disrupt the client service’s operation. Specify such local resources in the Location Exceptions section.
A request will be sent to the whitelist if its path to your resource contains a segment specified in this setting.
For example, when adding the path “/location” to the whitelist, requests such as the following will be executed without additional checks:
- site.com/location
- site.com/location/
- site.com/location.php
- site.com/location.php?id=123
- site.com/admin/location
Meanwhile, requests like the following will still be processed according to the general rules:
- site.com/some-other-location
- site.com/en_location.php
Click on the Add location button and fill out the form that appears.
Header Filter
You can create rules to block requests containing a specific header, as well as rules to allow them.
This feature is especially useful when working with APIs (where requests are made by a separate application). You can specify either a single header or a combination of several.
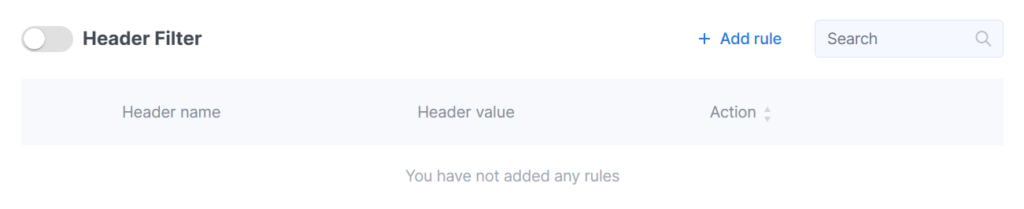
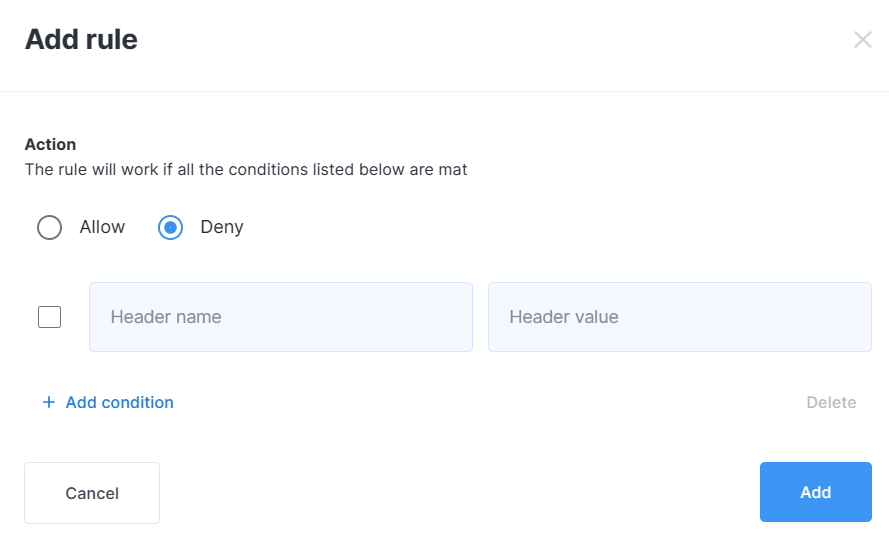
Click on the Add rule button and fill out the form.
Location filter
You can set up filtering for different locations of your resource.
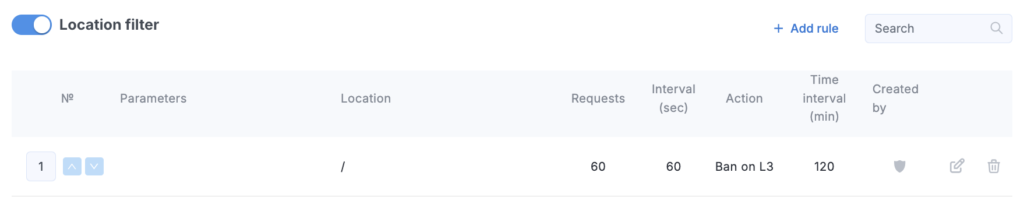
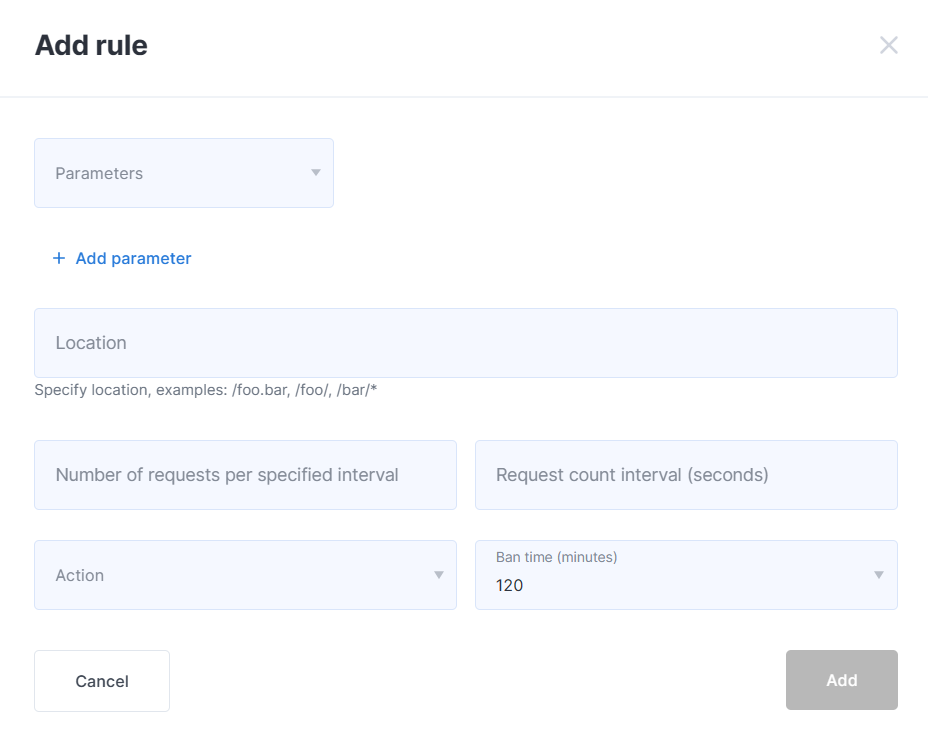
Click on the Add rule button and complete the form.
Advanced settings
Experienced users can independently configure a wide range of sensor parameters.
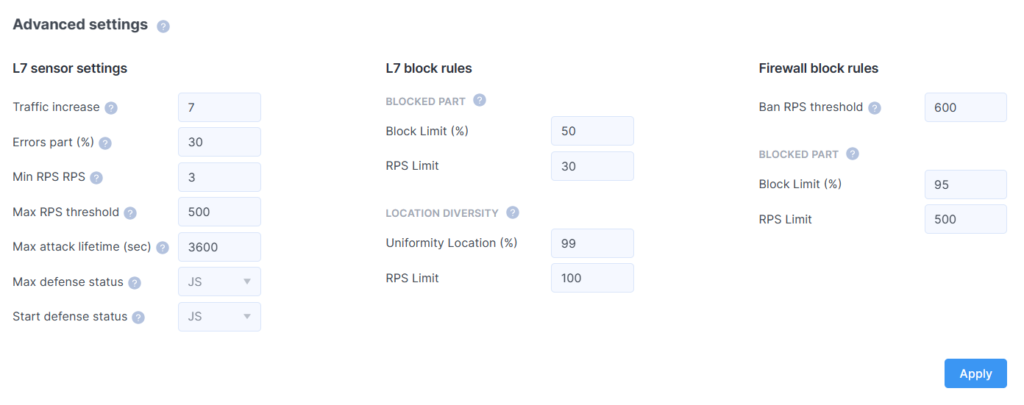
You have the option to configure:
- L7 sensor setting
In the first column, you can adjust parameters for attack detection:
- Traffic Increase: The factor by which the number of requests must increase over a short period of time to switch to active protection mode.
For example, the number “3” in this field will mean that the protection will be activated if the number of requests triples over the last 15 minutes.
- Errors Part: The percentage of erroneous requests that, once reached, will trigger the filters to switch to active mode.
For example, the number “30” in this area means that if the proportion of errors with “500” series codes exceeds the set value (30%), protective measures will be activated.
- Set Min RPS: The value below which “Traffic Increase” and “Errors Part” checks will not be performed.
- Max RPS Threshold: The number of requests that, when exceeded, triggers the switch to active mode.
- Max Attack Lifetime (sec): The time after the start of an attack after which the filter will attempt to switch back to sensor mode.
Here, you can specify the duration for which countermeasures against an attack are activated upon its detection, regardless of whether it has ceased or is continuing. This is a relevant parameter for combating attacks that are sporadic over time.
- Max Defence Status: The maximum type of protection during automatic trigger operations.
- Start Defence Status: The type of protection that will be set when the filter initially switches from sensor mode to active mode.
- L7 block rules
In the second column, you can set values to detect bot activity.
IIf more requests are received from an IP address than specified in the RPS Limit, and the percentage of blocked requests exceeds the Block Limit value, the system automatically identifies this address as a source of malicious activity and applies a block at the application level (L7). As a result, a user from this IP will be presented with an error page instead of the website.
- Blocked part
- Block Limit (%)
- RPS Limit
- Location diversity
- Uniformity Location (%)
- RPS Limit
- Firewall block rules
In the third column, the parameters of the firewall are presented.
Here, you can configure threshold values at the network level to block traffic from certain nodes, subnets, and networks without activating application-level filtering mechanisms.
- Ban RPS threshold
If a parameter is exceeded, then the IP address is blocked without additional checks.
- Blocked part L3 (%)
If the “RPS Limit” value is exceeded and the proportion of blocked requests from that IP address surpasses the “Block Limit”, then the address is blocked.
- Block Limit (%)
- RPS Limit




















